It’s a very important skill to learn how to remote control a robot in the robotics area. Our current technology is capable of creating millions of different machines with more skills than any other being on our planet. Although the top computers cannot even be compared to the human brain in terms of autonomy, it is a fact that they could perform very efficient when they have the human brain as a driver.
This project’s machine, glove plus robotic arm, uses Xbee modules to establish a communication channel between the devices. The “Arduino wireless shield” allows the Arduino board to transmit wireless using ZigBee, with a very reliable and simple communication. The protocol could be applied to almost any device with a serial port. Point to point or multi-point networks are supported too.
The glove is fitted with flex sensors (2.2”) to measure the movement of the fingers. Flex sensors, also called bend sensors, measure the amount of deflection caused by bending. These sensors can vary largely in terms of their range of resistance, measured as the difference from nominal resistance to resistance at full deflection.
One side of the sensor is printed with a polymer ink that has conductive particles embedded in it. When the sensor is straight, the particles give the ink a resistance of about 30k Ohms. When the sensor is bent away from the ink, the conductive particles move further apart, increasing this resistance (to about 50k). When the sensor straightens out again to his original state, the resistance returns to the original value too.
The below figure shows the block diagram for the glove part, device 1. The sensor measures the fingers position and through the Xbee module which is attached on the Arduino board transmits the information and waits for the device 2 to receive it.

Jointed arm robots are suitable for a wide variety of industrial tasks, ranging from welding to assembly and this is the main reason why I decided to build and remote control a robotic arm. Now there only two decisions left to make it possible, what kind of material is the best possible option for the body and the base and which motors suits the project’s needs.
The best material to build a small robotic arm is aluminum. Aluminum arms are strong, stable and cheap. I have found individual parts to buy online, these parts have numerous mounting holes which helped me to make a custom robotic arm using standard servo motors. Finally servo motors can be tricky, I have used one analog servo motor for the base, to rotate 360° and three digital servo motors for the joints and the claw. Digital servos can be extremely accurate but more expensive rotating usually 90° or 180°. Both types are useful but both of them have to be strong enough for their job. Keep in mind that for this type of arms, some servos have to lift others too. That’s why I had to calculate the amount of torque we would need. You must make sure that the motor can not only support the weight of the robot itself, but also what the robotic arm will carry when its stretched out to its maximum length.
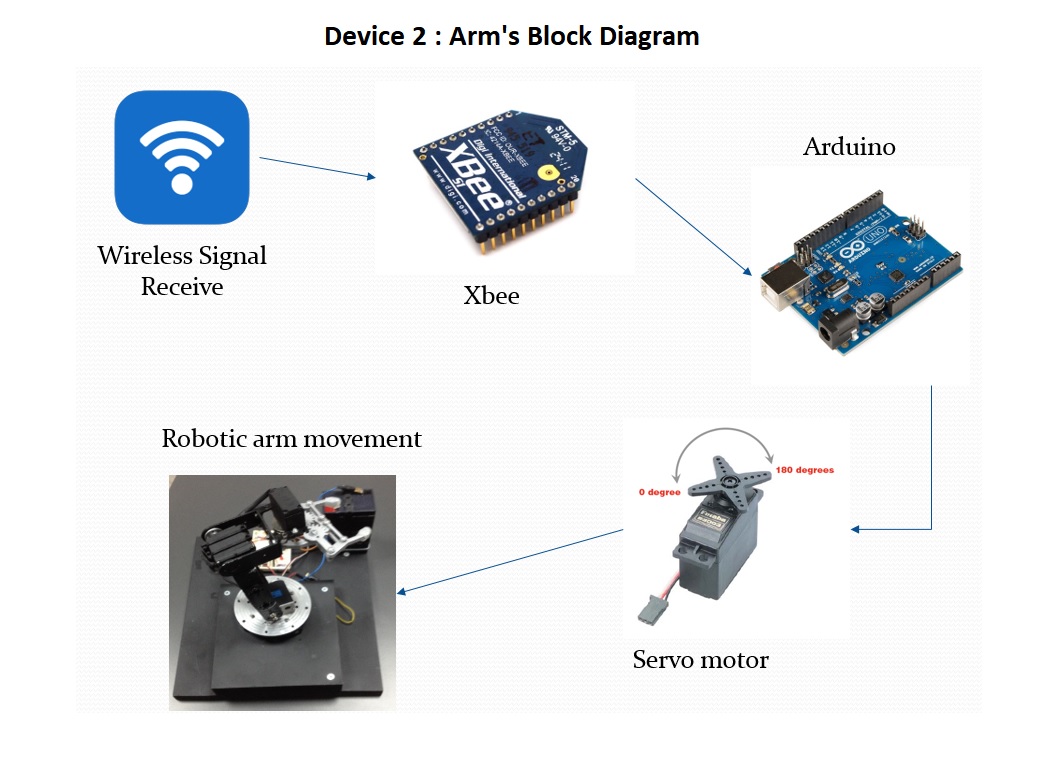
The below figure illustrates the robotic arm’s block diagram. After the information has been received by the device 2 with the use of the Xbee module attached to the second Arduino, the controller translates it into a movement for the appropriate servo motor, according to the finger move. The result is the movement of the robotic arm.